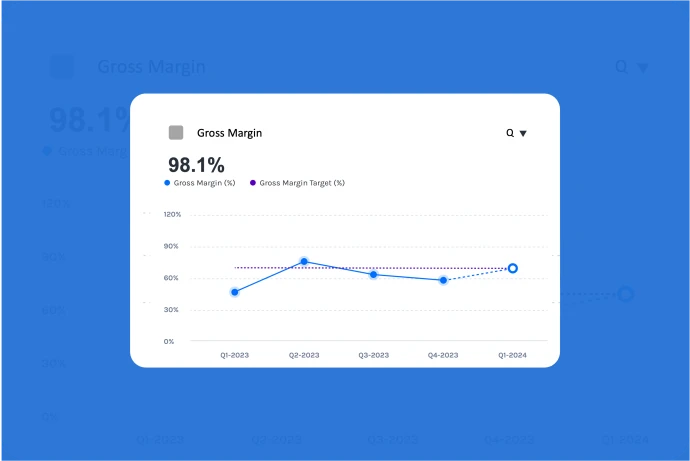
What is the Gross Margin?
Gross margin is a simple way to measure how much money a business keeps after covering the direct costs of making or delivering its product or service. To find it, you subtract the cost of providing the product (like materials or labor) from the money the business made from selling it. The result shows how much money is left to cover other expenses like marketing, salaries, and profit.
A higher gross margin means the business is keeping more money from each sale, which is a good sign of efficiency. It’s typically shown as a percentage, making it easy to compare across different periods or products.
Why is Gross Margin important?
Measuring Gross Margin is crucial for assessing a company’s ability to generate profit from its core business activities. It helps in understanding the relationship between the cost of goods sold (COGS) and revenue, providing insights into the efficiency of the production or procurement process. A healthy gross margin is essential for covering operating expenses and contributing to net profit.
How do you calculate the Gross Margin ?
Gross Margin is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue, then dividing the result by total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage. The formula is as follows:
Gross Margin Formula
((Total Revenue − COGS) / Total Revenue) ×100
How do you improve Gross Margin ?
Improving Gross Margin involves strategies that enhance the efficiency of the production or procurement process and optimize pricing strategies.
- One key approach is negotiating favorable terms with suppliers to secure better pricing for raw materials or components. Efficient supply chain management and inventory control can also contribute to cost savings and improved gross margins.
- Exploring pricing strategies that align with market demand and customer expectations is essential for optimizing gross margin. Companies may consider value-based pricing, premium offerings, or bundling strategies that enhance the perceived value of products, allowing for higher pricing and improved margins.
- Regularly reviewing and optimizing the product mix can also contribute to improved gross margin. Focusing on higher-margin products or services, phasing out low-margin offerings, and identifying opportunities for upselling or cross-selling can positively impact overall profitability.
- Investing in technology and automation to improve operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize errors in the production process is another strategy for enhancing gross margin. Continuous monitoring of industry trends, cost structures, and competitor pricing allows companies to make informed decisions and stay competitive in the market.
In summary, improving gross margin requires a combination of efficient cost management, strategic pricing, and continuous process optimization. Regularly assessing and adapting these strategies based on market dynamics and business performance contributes to sustained improvements in gross margin over time.