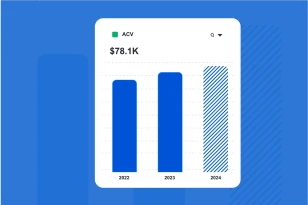
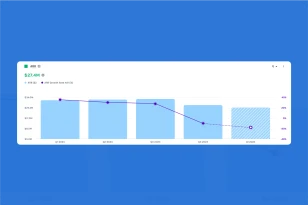
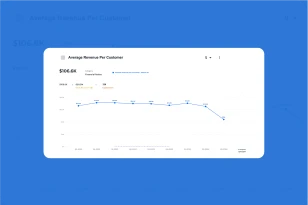
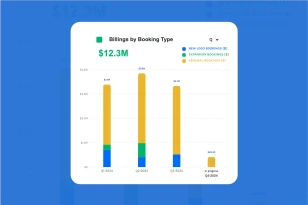
What is OPEX?
OPEX, short for Operating Expenses, refers to the ongoing costs that a business incurs as part of its normal operations. These expenses are distinct from capital expenditures (CAPEX), which involve significant investments in assets like equipment, facilities, or property. Operating expenses are incurred regularly and are necessary for the day-to-day functioning of a business.
Why is it Important to Measure OPEX?
Measuring Operating Expenses is crucial for businesses to understand and manage their financial health. OPEX represents the costs associated with running the core operations of the business, and monitoring these expenses is essential for budgeting, financial planning, and assessing overall profitability. Understanding and managing OPEX effectively contribute to maintaining financial sustainability and making informed business decisions.
How Do you Calculate OPEX?
Operating Expenses encompass various categories of costs, and the calculation involves summing up these costs.
Here’s a breakdown of the components:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs associated with producing goods or services, including raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses (SG&A): Indirect operating costs related to selling products or services and managing the overall business. This includes expenses such as marketing, sales salaries, rent, utilities, and office supplies.
- Other Operating Expenses: Various additional operating expenses that may include research and development costs, legal fees, and other miscellaneous costs necessary for ongoing operations.
How To Control or Manage OPEX?
Effectively managing OPEX involves strategies to control costs without compromising the quality of operations. Here are key approaches:
- Cost Efficiency: Regularly review and optimize processes to enhance cost efficiency. Identify areas where processes can be streamlined, and resources can be used more effectively.
- Expense Tracking: Implement robust systems for tracking and monitoring expenses. This includes using accounting software, budgeting tools, and financial reporting systems to gain visibility into spending patterns.
- Negotiate Contracts: Negotiate favorable terms with suppliers and vendors to secure better pricing for goods and services. Explore opportunities for bulk purchasing or long-term agreements to reduce costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-efficient practices to reduce utility costs. This may include investing in energy-efficient appliances, optimizing lighting, and adopting sustainable practices.
- Remote Work Policies: Consider remote work arrangements to reduce costs associated with office space and related expenses. Remote work can contribute to cost savings and increased employee satisfaction.
- Technology Optimization: Leverage technology to automate processes and reduce manual labor. Explore cost-effective technology solutions that align with business needs.
- Benchmarking: Compare operating expenses with industry benchmarks to identify areas where the company may be overspending. Benchmarking provides insights into industry standards and best practices.
- Training and Development: Invest in training and development programs to enhance employee skills and efficiency. Well-trained employees are often more productive and contribute to cost savings in the long run.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of operating expenses and budgetary allocations. This allows for timely identification of cost overruns or areas where adjustments may be necessary.
By adopting a proactive approach to cost management and continuously seeking opportunities for efficiency, businesses can control and manage their operating expenses effectively. Regular monitoring and adaptation of cost-control strategies contribute to financial stability and long-term success.